Polymerization
A polymer is a long chain molecule that consists of many repeating smaller molecules, referred to as monomers. A polymerization reaction is the process of the smaller monomers reacting to form the larger polymer. Polymerization can occur through a number of different methods depending on the size, shape, and functional groups of the monomers.
Examples:
1. The reaction of ethylene to form an alkane.
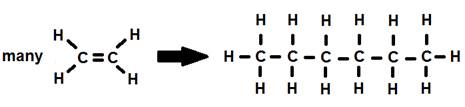
Note: This reaction continues with the number of ethylene molecules to produce larger and larger alkanes.
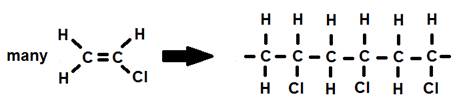
2. The reaction of chloroethene (vinyl chloride) to produce polyvinyl chloride (PVC).
Examples:
1. The reaction of ethylene to form an alkane.

Note: This reaction continues with the number of ethylene molecules to produce larger and larger alkanes.
2. The reaction of chloroethene (vinyl chloride) to produce polyvinyl chloride (PVC).

|
Related Links: Chemistry Organic Chemistry Transition Metals |
To link to this Polymerization page, copy the following code to your site:
