Condensation Reactions
A condensation reaction is an organic reaction in which two smaller molecules combine to form a larger molecule and a much simpler molecule. The simpler molecule produced is often water, which is why the phrase "condensation reaction" is used, while sometimes being referred to as a dehydration. Condensation reactions are important for the creation of many important biological molecules, such as carbohydrates and proteins.
Examples:
1. The reaction of two identical molecules:
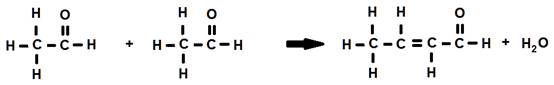
When two identical molecules combine to produce a condensation reaction, it is known as intramolecular condensation or self-condensation.
2. The reaction of two different molecules:
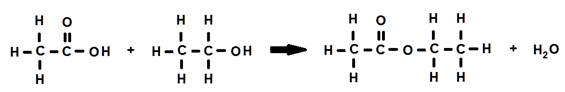
When two different molecules combine to produce a condensation reaction, it is known as intermolecular condensation.
Examples:
1. The reaction of two identical molecules:

When two identical molecules combine to produce a condensation reaction, it is known as intramolecular condensation or self-condensation.
2. The reaction of two different molecules:

When two different molecules combine to produce a condensation reaction, it is known as intermolecular condensation.
|
Related Links: Chemistry Organic Chemistry Constitutional Isomerism Cyclic Hydrocarbons |
To link to this Condensation Reactions page, copy the following code to your site:
