Constitutional Isomerism
Constitutional isomers (also known as structural isomers) are molecules that have the same chemical formula but their atoms are arranged differently. This altered arrangement of atoms causes the isomers to react differently and have different properties. There are three main types of constitutional isomers.
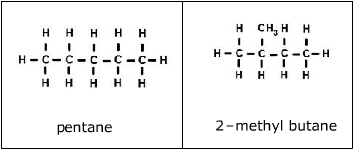
1. Chain isomers - the carbon chain has a different order of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
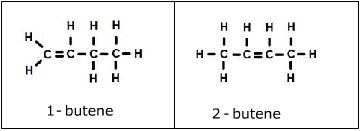
2. Position isomers - a functional group of the isomers is in a different location on the molecules.
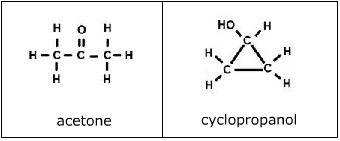
3. Functional Group Isomers - the isomers contain a different functional group.
1. Chain isomers - the carbon chain has a different order of carbon and hydrogen atoms.

2. Position isomers - a functional group of the isomers is in a different location on the molecules.

3. Functional Group Isomers - the isomers contain a different functional group.

|
Related Links: Chemistry Organic Chemistry Cyclic Hydrocarbons Isomers |
To link to this Constitutional Isomerism page, copy the following code to your site:
