Reference Angles
A reference angle is the smallest angle that is formed by the x- axis and the terminal side of the angle θ. Therefore, the reference angle is always coterminal with the original angle θ. Reference angles will always have a value between 0° and 90°. In the diagram below θ represents the original angle and R represents the Reference Angle
Quad I Reference AngleQuad II ReferenceAngle
Same as θ 180 - θ
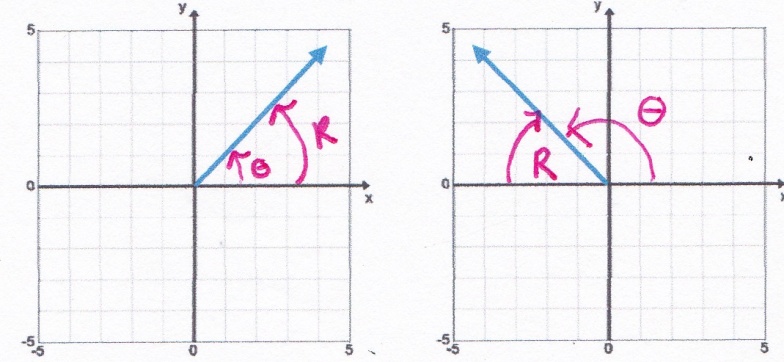
θ = 45° and R = 45°θ = 135° and R = 180° - 135° = 45°
Quad III Reference AngleQuad IV Reference Angle
θ - 180360 - θ
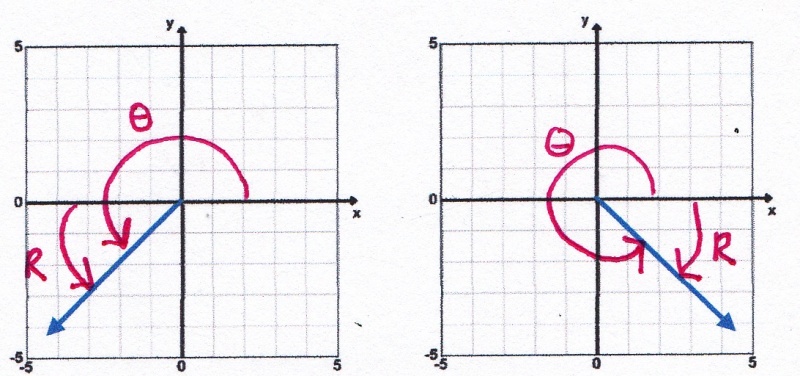
θ = 225° and θ = 315° and
R = 225 - 180 = 45 R = 360 - 315 = 45
The reference angle for any angle θ in standard position is the positive acute angle between the terminal side of θ and the x-axis. The reference angle is always positive and always between 0° and 90°
|
Related Links: Math Trigonometry Coterminal Angles Functions of Large and Negative Angles |
To link to this Reference Angles page, copy the following code to your site:
