Functions of Large and Negative Angles
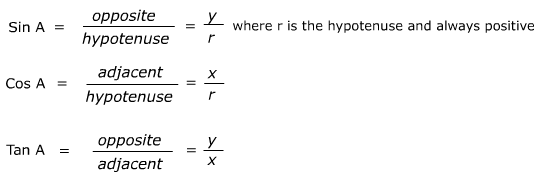
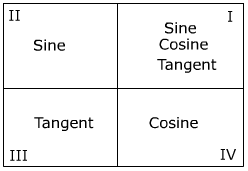
This leads to the functions being positive in the following quadrants.
Let's look at an example of a large angle. Consider the following graph of a 200° angle. A right triangle is created using the x axis and the terminal side of the angle.
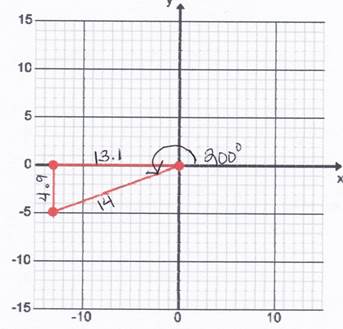
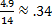 Therefore sin 200°
Therefore sin 200° 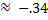 Because sine is negative in Quadrant III.
Because sine is negative in Quadrant III.Let's look at an example of a negative angle. Consider the graph of a -31° angle. A right triangle is created using the x axis and the terminal side of the angle.
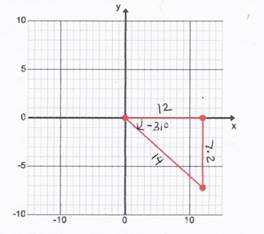
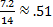 Therefore sin -31°
Therefore sin -31° 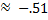 Because sine is negative in Quadrant IV.
Because sine is negative in Quadrant IV.Notice that the sine ratio still holds true with only a variance in sign based on the quadrant in which the terminal side of the angle lies. The same will also apply to the other trig ratios: cosine, tangent, secant, cosecant and cotangent.
|
Related Links: Math Trigonometry Inverse Trigonometric Functions Quadrantal Angles |
To link to this Functions of Large and Negative Angles page, copy the following code to your site:
