Double Angle Identities
|
cos2 θ = cos2θ - sin2θ sin2 θ = 2sin θ · cosθ cos2θ = 1 - 2 sin2θ 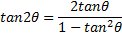 cos2θ = 2 cos2θ - 1 |
Example: If
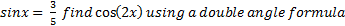
cos2x = 1 - 2 sin2 x
Substitute
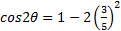
Simplify
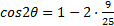
Simplify
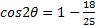
Simplify
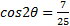
Example: Find all the solutions of 2 cosθ + sin2θ = 0 where
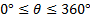
1) Replace sin2θ with 2sin θ · cos θ
2cosθ + 2sin θ · cos θ = 0
2) Factor out the common factor of 2 cosθ
2cos θ (1 + sinθ) = 0
3) Use the zero product rule
2 cos θ = 01 + sinθ = 0
cosθ = 0 sin θ = -1
4) Determine when cos θ = 0 and sin θ = -1
cos θ = 0 when θ is 90°
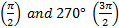
sin θ = -1 when

Therefore the solution set is 90°
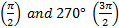
|
Related Links: Math Trigonometry Half Angle formulas Even and Odd Trig Functions Sum and Difference of Angles Identities |
To link to this Double Angle Identities page, copy the following code to your site:
