Angle Definition and Properties of Angles
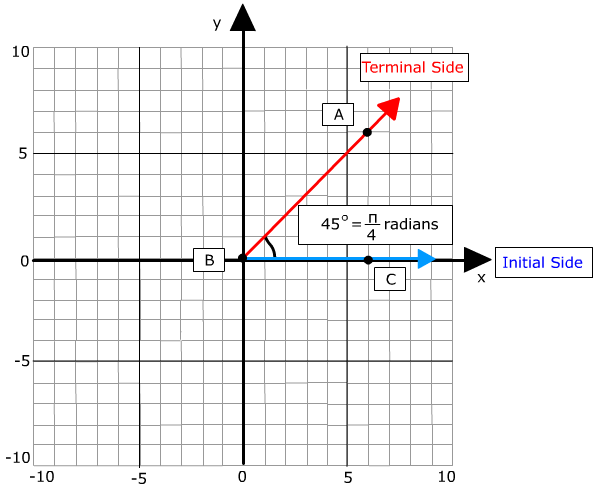
The angle can be named in two ways: (1) if there is only one angle the vertex can be used. For example: ∠B. (2) If there are multiple angles it is best to use three points. For example: ∠ABC using the vertex as the center letter. m∠B=45° means the measure of angle B is 45 degrees.
When rotating the terminal side counterclockwise the angle measure is positive. One full rotation beginning from the initial side is 360°. However, the terminal side can rotate numerous times creating very large angles. For example 720° would be two complete revolutions.
When rotating the terminal side clockwise negative angles are created. One full rotation beginning from the initial side is -360° (negative 360°). The terminal side can be rotated numerous times creating large negative numbers. For example if the terminal side rotated 3 times the degree measure would be 1080°.
|
Related Links: Math Trigonometry Introduction to the Six Trigonometric Functions (Ratios) Standard Position of an Angle - Initial Side - Terminal Side |
To link to this Angle Definition and Properties of Angles page, copy the following code to your site:
