Component Form and Magnitude
In this discussion vectors will be denoted by lowercase boldface variables. Examples of vector quantities are velocity, acceleration and force.
Figure 1 shows two vectors v and u as directed line segments.
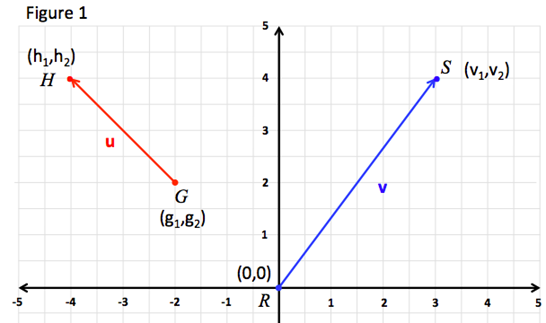
The vector v is represented by the directed line segment and has an initial point at R and a terminal point at S.
Vectors are often represented in component form. Vector v in Figure 1 has an initial point at the origin (0,0) and is said to be in standard position. A vector in standard position can be represented by the coordinates of its terminal point. Thus vin component form = .
The magnitude of v or is represented by or and is calculated using the Distance Formula, .
MAGNITUDE OF A VECTOR:
Vector u represented by in Figure 1 is not in standard position as its initial point is not the origin (0,0). The component form and magnitude of vector u can be calculated as follows:
COMPONENT FORM OF DIRECTED LINE SEGMENT:
Initial point: G (g1, g2)
Terminal Point: H (h1, h2)
MAGNITUDE OF DIRECTED LINE SEGMENT:
Initial point: G (g1, g2)
Terminal Point: H (h1, h2)
Let's look at a couple examples.
|
Step 1: Identify the initial and terminal coordinates of the vector. |
Initial Point G: (-2, 2) Terminal Point H: (-4, 4) |
|
|
Step 2: Calculate the components of the vector. Subtract the x-component of the terminal point from the x-component of the initial point for your x-component of the vector. Do the same for the y-components. |
|
|
|
Step 3: Calculate the magnitude of the vector. |
||u|| = ||u|| =
|
|
|
Step 1: Identify the initial and terminal coordinates of the vector. Because vector v is in standard position it's initial point is (0,0) |
Initial Point: (0, 0) Terminal Point: (8, -2) |
|
Step 2: Calculate the components of the vector. Subtract the x-component of the terminal point from the x-component of the initial point for your x-component of the vector. Do the same for the y-components. In this case the vector is in standard form therefore the components of the vector are the same as the components of the terminal point. |
|
|
Step 3: Calculate the magnitude of the vector. |
||v|| = ||v|| =
|
|
Related Links: Math algebra Scalar Multiplication and Vector Addition Unit Vectors Pre Calculus |
To link to this Component Form and Magnitude page, copy the following code to your site:
