Zinc (II) chloride Formula
Zinc (II) chloride, also known as butter of zinc, is an inorganic salt very soluble in water and mostly used in organic synthesis as catalyst and as disinfectant.
Formula and structure: Zinc chloride chemical formula is ZnCl2 and its molar mass is 136.15 g mol-1. The zinc chloride molecule is a binary salt formed by the zinc cation Zn+2 and chloride anion Cl- and it can be found as anhydrous or tetrahydrated form. The structure may be tetrahedral or orthorhombic depended on the hydration state. Its chemical structure can be written as below, in the common representations used for organic molecules.
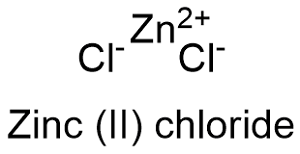
Occurrence: Zinc chloride is not found in nature, it is only obtained from chemical synthesis.
Preparation: Zinc chloride is obtained from reaction between a solution of hydrochloric acid and metallic zinc at 700 ºC:
Zn(s) + 2 HCl → ZnCl2 + H2(g)
If the zinc chloride is anhydrous, the samples are sublimated to eliminate the water.
Physical properties: Zinc chloride is a white hygroscopic crystalline solid. Its density is 1.01 g mL-1. Zinc chloride melting point is 162-172 ºC and its boiling point is 220 ºC. It is soluble in water, ethanol, glycerol and acetone.
Chemical properties: Zinc chloride is mostly thought as a ionic compound, however it has been determinate it has a behavior more covalent. The difference of electro-negativity between Zinc and Chloride is 1.3, which is not enough to form a strong ionic bond. For that reason the melting point (energy required to break the bonds) is lower than ionic salts as sodium chloride. The zinc chloride can react in diverse ways, all of them are similar to the reaction showed by the covalent compounds, for example: the formation of complex with water molecule or in the presence of alkali solution when are formed complex species such as: Zn(OH)3Cl2-, Zn(OH)2Cl2- or ZnOHCl2-.
Uses: Zinc chloride can be used to treat cellulose and other biopolymers such as starch, thus it has been largely apply in the textile and paper industries. Moreover, zin chloride has been used as disinfectant to prepare the Burnett's Disinfecting Fluid. Zinc chloride has also many applications as catalysts in organic synthesis, especially to promote reaction such as Friedels-Crafts acylations.
Health effects / safety hazards: Zinc (II) chloride is an irritant to eyes, skin and mucous. It is not flammable, however, when heated toxic and combustible cobalt oxides fumes are emitted. It is corrosive.
|
Related Links: |
