Gay-Lussac's Law Formula
Gay-Lussac's Law shows the relationship between the Temperature and Pressure of a gas. At a fixed volume, the temperature and pressure of a gas are directly proportional to each other. Since temperature and pressure have a direct relationship, if the pressure goes up then the temperature goes up and if the temperature goes down then the pressure goes down (and vice versa)
The equation for Gay-Lussac's Law is:
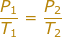
T1 = Initial Temperature (Kelvin - K)
P1 = Initial Pressure (atm or mmHg)
T2 = Final Temperature (Kelvin - K)
P2 = Final Pressure (atm or mmHg)
Note: Temperature must be in Kelvin for the equation to work. You calculate Kelvin temperature by adding 273 to the Celsius temperature.
Gay-Lussac's Law Formula Questions:
1.) A gas has a pressure of 699.0 mm Hg at 40.0 °C. What is the temperature at a pressure of 760.0 mm Hg?
Answer: For this problem the Initial Pressure is P1 = 699.0 mmHg. The Initial Temperature is T1 = 40.0 + 273 = 313K. The Final Pressure is P2 = 760.0 mmHg and the Final Temperature (T2 ) is what you are asked to solve for.
Plug into the Gay-Lussac's Law Equation
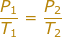
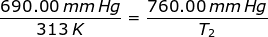
T2 = 344.75 K
The temperature increased to 344.75 K.
2.) Determine the pressure change when a constant volume of gas at 1.00 atm is heated from 20.0 °C to 30.0 °C.
Answer: The Initial Pressure is P1 = 1.00 atm. The Initial Temperature is T1 = 20.00 + 273 = 293 K. The Final Temperature is T2 = 30.0 + 273 = 303 K. The Final Pressure (P2) is what we are trying to find in the problem.
Plug into the Gay-Lussac's Law Equation
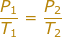
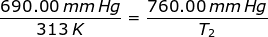
P2 = 1.03 atm
The pressure of the container increased to would be 1.03 atm.
