Alkenes
Alkenes are a group of organic hydrocarbons that contain a carbon to carbon double bond. Because of this double bond, the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbons is reduced. For this reason, alkenes are called unsaturated and have the generic formula, CnH2n. The name alkene (with suffix ~ene) as opposed to alkane, implies that a carbon to carbon double bond will be found within the organic molecule.
Alkenes play a major role in modern and biological chemistry. Beta-carotene, for example, is a very important part of human diet as a source of vitamin A. Ethylene and propylene, sometimes referred to as ethene and propene respectively, are the two most industrially produced organic chemicals. They are used in the production of many raw materials, including plastics.
The number of reactions that can take place in the double bonded area of the alkene is staggering. The carbon to carbon double bond supplies the alkene with an electron rich source for further reactions. This extra pair of electrons in the pi bond (double bond) of the alkene will often react with neighboring molecules that are electron deficient. Many synthesis reactions in organic chemistry stem from this.
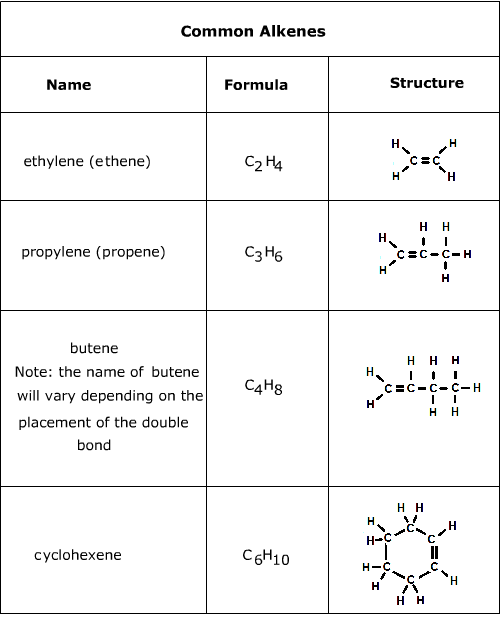
Alkenes play a major role in modern and biological chemistry. Beta-carotene, for example, is a very important part of human diet as a source of vitamin A. Ethylene and propylene, sometimes referred to as ethene and propene respectively, are the two most industrially produced organic chemicals. They are used in the production of many raw materials, including plastics.
The number of reactions that can take place in the double bonded area of the alkene is staggering. The carbon to carbon double bond supplies the alkene with an electron rich source for further reactions. This extra pair of electrons in the pi bond (double bond) of the alkene will often react with neighboring molecules that are electron deficient. Many synthesis reactions in organic chemistry stem from this.

|
Related Links: Chemistry Organic Chemistry Alkynes |
To link to this Alkenes page, copy the following code to your site:
