Addition Reactions
An addition reaction occurs in organic chemistry when two smaller organic molecules combine to form a larger one. They are limited to organic molecules that contain multiple bonds, therefore, alkenes and alkynes are most likely involved. Functional groups that contain multiple bonds are also susceptible to addition reactions, such as molecules with carbon to oxygen double bonds. The pi bond of the alkene or other multiple bonded organic molecules offers electrons to molecules that are in search of extra electrons (electrophiles).
Examples:
1. Addition of bromine to ethylene
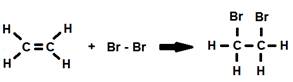
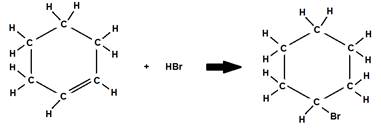
2. Addition of an acid to cyclohexene
Examples:
1. Addition of bromine to ethylene

2. Addition of an acid to cyclohexene

|
Related Links: Chemistry Organic Chemistry Alkanes vs. Alkenes vs. Alkynes Aromatic Hydrocarbons |
To link to this Addition Reactions page, copy the following code to your site:
