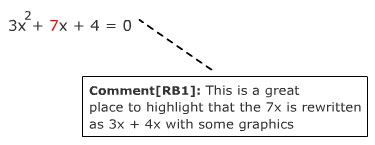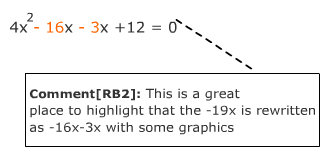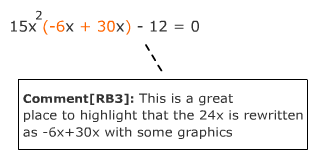Factoring Quadratic Equations when a ≠ 1
Where a, b, and c are constants and a ≠ 0. In other words there must be a x2 term.
Some examples are:
x2 + 3x - 3 = 0
4x2 + 9 = 0 (Where b = 0)
x2 + 5x = 0 (where c = 0)
One way to solve a quadratic equation is by factoring the trinomial.
PART I of this topic focused on factoring a quadratic when a, the x2-coefficient, is 1.
This part, PART II will focus on factoring a quadratic when a , the x2-coefficient, is not 1.
Where q, r, s and t are constants.
Let's solve the following equation by factoring the trinomial:
|
Step 1: Write the equation in the general form ax2 + bx + c = 0. This equation is already in the proper form where a = 3, b = 7 and c = 4. |
3x2 + 7x + 4 = 0 |
|
Step 2: Multiple a · c and find the factors of the result, let's call this p. |
a = 3, c = 4 3 · 4 = 12 = p |
|
Step 3: Determine the factor pairs of p that will add to b. 3.1: List the factor pairs of p. First ask yourself what are the factors pairs of p, ignoring the negative sign for now. 3.2: Determine the signs of the factors. If p is positive then both factors will be positive or both factors will be negative. If p is negative then one factor will be positive and the other negative. 3.3: Determine the factor pair that will add to give b. If both p and b are positive, both factors will be positive. If both p and b are negative, the larger factor will be negative and the smaller will be positive. If p is positive and b is negative, both factors will be negative. If p is negative and b is positive, the larger factor will be positive and the smaller will be negative. |
(1, 12);(2, 6);(3, 4)
These pairs do not work.
This pair works!!! (3, 4) |
|
Step 4: Rewrite bx as a sum of two x-terms using the factor pair found in Step 3. |
3x2 + 3x + 4x + 4 = 0 |
|
Step 5: Group the terms for factoring. |
(3x2 + 3x) + (4x + 4) = 0 |
|
Step 6: Factor the greatest common denominator from each group. |
3x(x + 1) + 4(x + 1) = 0 |
|
Step 7: Rewrite the equation as two polynomial factors.
Notice that the parenthetical expression is the same for both groups. If this does not occur, regroup the terms and try again. Using the reverse of the distributive property we can write the outside expressions (shown in red in Step 6) as a second polynomial factor. |
(3x + 4)(x + 1) = 0 |
|
Now that the equation has been factored, solve for x. |
|
|
Step 8: Set each factor to zero and solve for x. |
(3x + 4) = 0, or (x + 1) = 0 , or x = -1 |
|
Step 1: Write the equation in the general form ax2 + bx + c = 0. This equation is already in the proper form where a = 4, b = -19 and c = 12. |
4x2 - 19x + 12 = 0 |
|
Step 2: Multiple a · c and find the factors of the result, let's call this p. |
a = 4, c = 12 4 · 12 = 48 = p |
|
Step 3: Determine the factor pairs of p that will add to b. 3.1: List the factor pairs of p. First ask yourself what are the factors pairs of p, ignoring the negative sign for now. 3.2: Determine the signs of the factors. If p is positive then both factors will be positive or both factors will be negative. If p is negative then one factor will be positive and the other negative. 3.3: Determine the factor pair that will add to give b. If both p and b are positive, both factors will be positive. If both p and b are negative, the larger factor will be negative and the smaller will be positive. If p is positive and b is negative, both factors will be negative. If p is negative andb is positive, the larger factor will be positive and the smaller will be negative. |
(1, 48);(2, 24);(3, 16);(4, 12);(6, 8)
These pairs do not work.
This pair works!!! (-3, -16) |
|
Step 4: Rewrite bx as a sum of two x-terms using the factor pair found in Step 3. |
4x2 - 19x + 12 = 0
|
|
Step 5: Group the terms for factoring. |
(4x2 -16x) + (-3x + 12) = 0 |
|
Step 6: Factor the greatest common denominator from each group. |
4x(x - 4) - 3(x - 4) = 0 |
|
Step 7: Rewrite the equation as two polynomial factors.
Notice that the parenthetical expression is the same for both groups. If this does not occur, regroup the terms and try again. Using the reverse of the distributive property we can write the outside expressions (shown in red in Step 6) as a second polynomial factor. |
(4x - 3)(x - 4) = 0 |
|
Now that the equation has been factored, solve for x. |
|
|
Step 8: Set each factor to zero and solve for x. |
(4x - 3) = 0, or (x - 4) = 0 , or x = 4 |
|
Step 1: Write the equation in the general form ax2 + bx + c = 0. This equation is already in the proper form where a = 15, b = 24 and c = -12. |
15x2 + 24x - 12 = 0 |
|
Step 2: Multiple a · c and find the factors of the result, let's call this p. |
a = 15, c = -12 15 · (-12) = -180 = p |
|
Step 3: Determine the factor pairs of p that will add to b. 3.1: List the factor pairs of p. First ask yourself what are the factors pairs of p, ignoring the negative sign for now. 3.2: Determine the signs of the factors. If p is positive then both factors will be positive or both factors will be negative. If p is negative then one factor will be positive and the other negative. 3.3: Determine the factor pair that will add to give b. If both p and b are positive, both factors will be positive. If both p and b are negative, the larger factor will be negative and the smaller will be positive. If p is positive and b is negative, both factors will be negative. If p is negative and b is positive, the larger factor will be positive and the smaller will be negative. |
(1,180);(2,90);(3,60);(4,45);(5,36);(6,30); (9,20);(10,18);(12,15)
These pairs do not work.
This pair works!!! (-6, 30) |
|
Step 4: Rewrite bx as a sum of two x-terms using the factor pair found in Step 3. |
15x2 + 24x - 12 = 0
|
|
Step 5: Group the terms for factoring. |
Grouping 1: (15x2 -6x) + (30x - 12) = 0 OR Grouping 2: (15x2 + 30x) +(-6x + 12) = 0 |
|
Step 6: Factor the greatest common denominator from each group. |
Grouping 1: 3x(5x - 2) + 6(5x - 2) = 0 OR Grouping 2: 15x(x + 2) - 6(x - 2) = 0 |
|
Step 7: Rewrite the equation as two polynomial factors.
Notice that the parenthetical expression is the same for both groups. If this does not occur, regroup the terms and try again. Using the reverse of the distributive property we can write the outside expressions (shown in red in Step 6) as a second polynomial factor. |
Grouping 1: (3x + 6)(5x - 2) = 0 Grouping 2: (15x - 6)(x + 2) = 0 |
|
Now that the equation has been factored, solve for x. |
|
|
Step 8: Set each factor to zero and solve for x. |
Grouping 1: (3x + 6) = 0, or (5x - 2) = 0 , or
Grouping 2:
(15x - 6) = 0, or (x + 2) = 0
, or x = -2
In either case the answer is the same. |
Factoring quadratics is generally the easier method for solving quadratic equations. However, not all quadratic equations can be factored evenly. In these cases it is usually better to solve by completing the square or using the quadratic formula.
|
Related Links: Math algebra Quadratic Formula The Difference of Perfect Squares Algebra Topics |
To link to this Factoring Quadratic Equations when a ≠ 1 page, copy the following code to your site: