Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Aromatic hydrocarbons are cyclic hydrocarbons that have alternating double and single bonds. The term "aromatic" was used not because of their structure but because many of these compounds have a smell (aroma). The name stuck to decrease the confusion surrounding this class of hydrocarbon.
The simplest aromatic hydrocarbon is benzene. It consists of six carbons in a ring. The formula for benzene is C6H6 with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom in the ring.
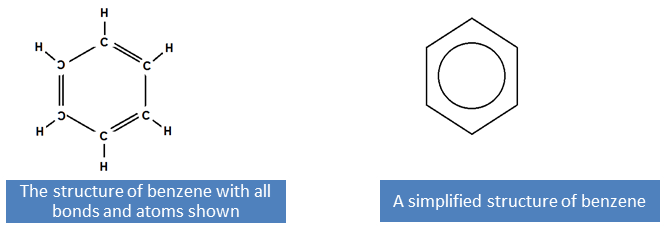
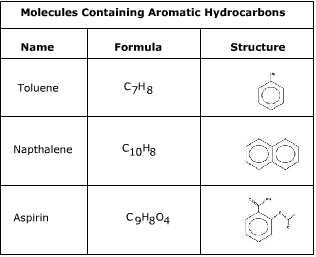
Benzene rings are the building blocks of aromatic hydrocarbons and can be seen in many structures.
The simplest aromatic hydrocarbon is benzene. It consists of six carbons in a ring. The formula for benzene is C6H6 with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom in the ring.

Benzene rings are the building blocks of aromatic hydrocarbons and can be seen in many structures.

|
Related Links: Chemistry Organic Chemistry Condensation Reactions Constitutional Isomerism |
To link to this Aromatic Hydrocarbons page, copy the following code to your site:
